We’re nearer than ever to mapping all the mind to the microscopic stage. Tons of of neuroscientists the world over lately characterised greater than 3,000 human mind cell sorts as a part of the National Institute of Health’s BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network, publishing nearly two dozen papers in 4 Science journals at this time. This super-focused consideration to element may unlock many mysteries surrounding that complicated organ, equivalent to what occurred in our brains to differentiate us from different primates.
“That is the primary large-scale, detailed description of all of the completely different sorts of cells current within the human mind,” says Rebecca Hodge, an assistant investigator on the Allen Institute in Seattle who co-authored a number of research within the paper package deal. Her hope is that this mind atlas offers a group useful resource for scientists to discover how the wide range of mind cells contribute to well being and illness. This primary suite of research reveals three foremost methods the mind map can be utilized for biology and drugs.
An evolving mind
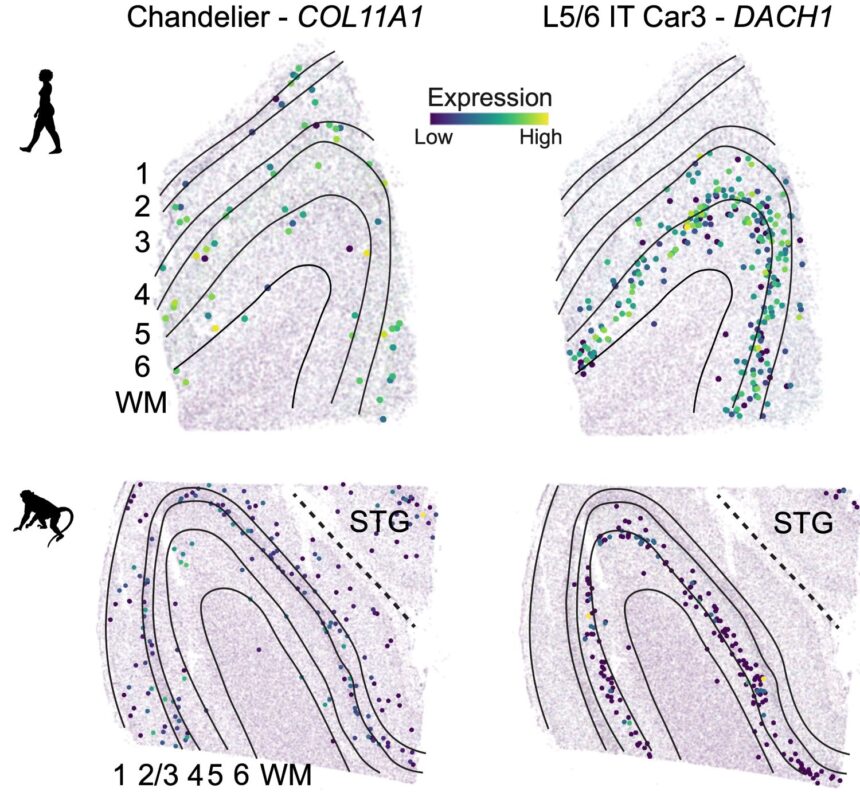
A human mind atlas can educate us about our evolutionary historical past. One study revealed at this time in Science used single-nucleus RNA sequencing to measure the gene expression of particular person mind cells in people and 5 different primate species, together with chimpanzees and gorillas. On this technique, scientists pull out particular person cells from a chunk of tissue, break them open to reveal the genetic messengers inside, then use tags akin to tiny barcodes to establish that materials. “That is the primary know-how utilized in a few of these papers which are popping out and it’s a way that’s solely been round for the previous 10 years,” Hodge says. Getting this genetic profile permits researchers to group clusters of cells into particular sorts.
[Related: Psychedelics and anesthetics cause unexpected chemical reactions in the brain]
Our cells’ composition and group is just like these of our shut kin. Nonetheless, the largest variations appeared to happen in a mind area referred to as the center temporal gyrus, which is concerned in processing semantic memory and language. People had increased numbers of projecting neurons on this space in comparison with different species. What’s extra, the researchers highlighted a distinction in gene expression that promoted synaptic plasticity, which is the flexibility of neurons to strengthen mind connections. This function is a crucial element for studying and reminiscence, and it would clarify how people developed complicated cognitive expertise.
There was some variation inside people, too. One other study discovered probably the most variations throughout people in immune cells referred to as microglia in addition to deep-layer excitatory neurons, that are concerned within the communication between distant mind areas. Researchers are usually not fairly certain why—one concept is that deep-layer excitatory neurons develop earlier and are extra uncovered to environmental elements that might diversify their gene patterns. “Everybody’s mind is basically comparable. Regardless that we now have the identical constructing blocks, it’s the small variety of variations that matter,” says Jeremy Miller, a senior scientist on the Allen Institute, and co-author of the examine. “We’re now beginning to perceive how necessary these modifications are and determining what makes us uniquely human.”
Animal fashions
As a result of human brains share many options with different mammals, neurologists steadily use the small brains of mice to review ailments. The one drawback, Miller says, is that mice don’t naturally develop neurodegenerative ailments frequent in people. Scientists who wish to examine Alzheimer’s illness, for instance, would wish to control a number of mouse genes to trigger the type of mind pathology seen in older individuals. This requires a complete understanding of how cell sorts within the mind work collectively and the way they modify within the context of illness.
[Related: How your brain conjures dreams]
A lot mind analysis in mice focuses on the neocortex, liable for increased cognitive perform. It may appear cheap to imagine that a lot of the mind’s mobile complexity seems right here. However this doesn’t appear to be the case. In one of the first studies to create a cell map of all the grownup mind, neuroscientists have discovered excessive ranges of variety in older evolutionary constructions such because the midbrain, which is concerned in motion, imaginative and prescient, and listening to, and the hindbrain, which governs important bodily features equivalent to respiration and coronary heart fee. In subcortical areas, there additionally seems to be a supercluster of cells referred to as splatter neurons that management innate behaviors and physiological features. Replicating the complexity of those explicit mind areas in animal fashions may assist higher establish the mobile origins of human ailments.
Personalised drugs
Think about a future the place therapies are tailor-made to somebody’s particular wants. To do this, scientists would use an individual’s genetic profile, quite than traits equivalent to weight or age, to tell any medical selections. Clinicians may additionally use this genetic data to establish the dangers of potential ailments and supply early preventative measures.
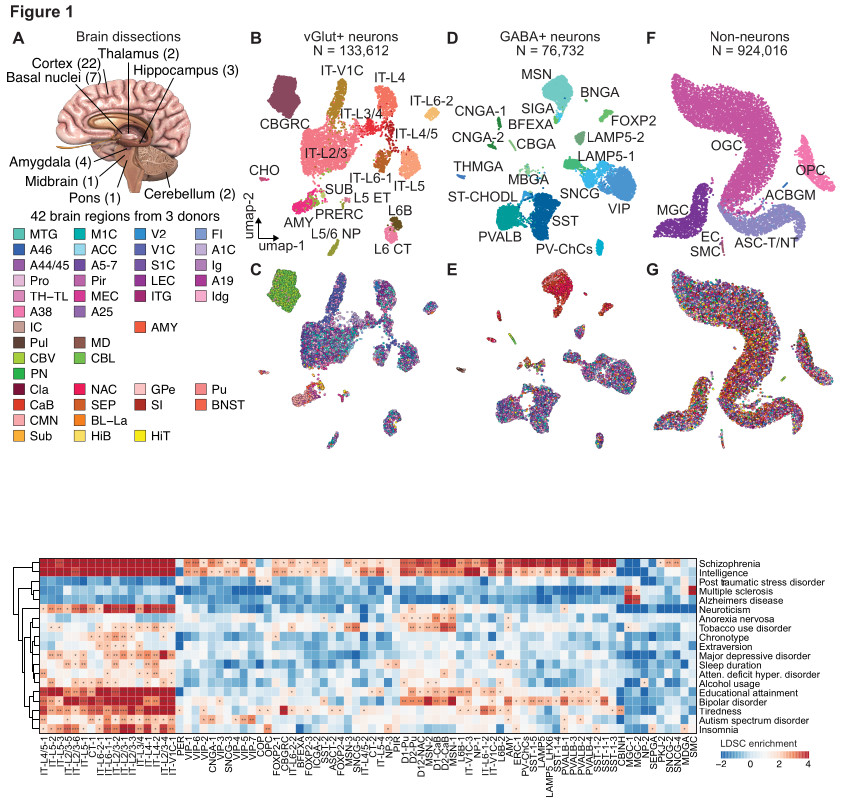
Medical doctors are already utilizing individuals’s genetic data to evaluate whether or not sufferers can be good candidates for a selected most cancers therapy or to search out the correct dose of a drug. This may occasionally quickly embody testing for neurological circumstances. One study, which analyzed 1.1 million cells in 42 mind areas of neurotypical adults, recognized particular neuronal cell sorts—primarily within the basal ganglia, a area concerned in addictive behaviors—that had been linked to 19 neuropsychiatric issues and traits. These circumstances included schizophrenia and bipolar dysfunction in addition to alcohol and tobacco use dysfunction.
This mission is a step in the proper route for advancing analysis in personalised drugs, says Miller, although he warns this is just one of many to make this a actuality for everybody.
Miller and Hodge are optimistic there will probably be different variations of the human mind atlas accomplished within the subsequent 5 years, as different teams wrap up comparable tasks.
However there’s a risk that we’ll by no means get the complete image. Whereas Miller finds a half-decade timeframe cheap, he says there’s at all times an opportunity science develops a brand new know-how that might unearth one thing surprising in regards to the mind. “We are able to at all times do extra,” he says.