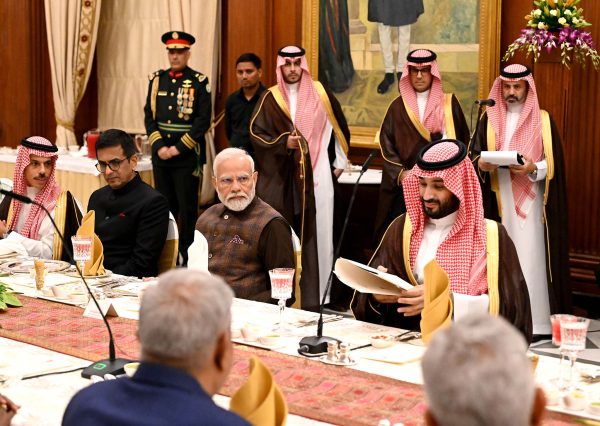
One achievement reached on the sidelines of India’s G-20 Summit was the brand new initiative to develop a rail and transport hall connecting India to Europe through the Center East. In accordance with a White Home fact sheet, leaders from the US, India, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, France, Germany, Italy, and the European Union signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) agreeing to determine a brand new India-Center East-Europe Financial Hall (IMEC).
That a few of the main Center Japanese nations together with Saudi Arabia, Israel, the UAE, and Jordan are a part of it makes it noteworthy, particularly from a geopolitical perspective. Announcing this on the G-20 Leaders’ assembly on the Partnership for World Infrastructure and Funding (PGII), the leaders famous that the IMEC will contain rail connectivity, transport traces, high-speed information cables, and power pipelines. These will complement the prevailing maritime and highway networks that may improve motion of commerce and companies “to transit to, from, and between India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel, and Europe.”
Particularly since China launched its Belt and Highway Initiative (BRI), the US and its companions have made efforts to give you efficient various proposals. The PGII, launched as a counter to China’s BRI on the G-7 Summit in August 2022, can also be an infrastructure initiative to fund connectivity initiatives in growing nations. Like IMEC, the PGII has 4 focus areas: well being and well being safety, digital connectivity, gender equality and fairness, and local weather and power safety. A yr later the MoU was signed, the PGII has a string of projects and investments.
Together with IMEC, the G-20 summit additionally noticed the European Union announce its plans for a “Trans-African Hall,” a transportation community linking Angola, Zambia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Trans-African Hall was described within the press launch as “a robust evolution” of the PGII.
IMEC is important from an infrastructure and connectivity perspective in addition to from a geopolitical angle. The undertaking includes two separate corridors – the east hall, which connects India to the Arabian Gulf, and the northern hall, which connects the Arabian Gulf to Europe. In accordance with the MoU, IMEC is “anticipated to stimulate financial improvement by enhanced connectivity and financial integration between Asia, the Arabian Gulf, and Europe.”
The brand new hall has different essential dimensions, together with dependable and safe regional provide chains, higher commerce accessibility, and commerce facilitation. The taking part nations need to “enhance efficiencies, cut back prices, improve financial unity, generate jobs, and decrease greenhouse gasoline emissions – leading to a transformative integration of Asia, Europe, and the Center East.”
Whereas particulars are nonetheless awaited, what’s at present recognized is that IMEC is exploring many various routes connecting a number of ports alongside the way in which, together with Haifa in Israel, Piraeus in Greece, and three ports on the west coast of India: Mundra (Gujarat), Kandla (Gujarat), and Jawaharlal Nehru Port Belief (Navi Mumbai). There are 5 ports within the Center East that may hyperlink up with the Indian ports and these embrace Fujairah, Jebel Ali, and Abu Dhabi within the UAE in addition to the Dammam and Ras Al Khair ports in Saudi Arabia. All of those are being shortlisted to make a closing determination that will likely be based mostly on the routes that may “prospectively reduce the freight load on one route.”
It ought to be famous that each one ports however the Mundra port in India, the Haifa port in Israel, and the Piraeus port in Greece are government-owned. The Mundra and Haifa ports are underneath the management of the Indian conglomerate, Adani Group. Greece’s Piraeus port is controlled by COSCO Shipping, a Chinese language state-owned enterprise, which obtained a majority stake in 2016.
In accordance with official sources cited in media stories, research are being carried out to determine the state of the infrastructure, particularly railway networks within the Center East. Missing links are being famous for contemporary building work underneath IMEC. The proposed value of IMEC isn’t obtainable, however one media report indicated that partnering nations “could allocate an estimated $20 billion” towards the financial hall. Different media stories have indicated an early estimate of $3 billion to $8 billion for growing every of the IMEC routes, though officers reportedly acknowledged that “it’s too early to peg prices.”
The nations that signed the MoU are to meet in November to begin firming up the main points.
In geopolitical phrases, IMEC is touted as a counter to China’s BRI, however the scale and scope of the BRI is way larger. Since its launch a decade in the past, over 150 nations and about 30 worldwide organizations have signed on to the BRI. India, from very early days, had objected to it as a result of the China-Pakistan Financial Hall, a key part of the BRI, runs by territories claimed by India. Although numerous nations have endorsed it, the BRI’s picture has been soured by debt woes in nations like Sri Lanka. Most lately, Italy introduced a call to drag out of the BRI as a result of it “did not deliver the outcomes anticipated.”
It’s tough for a single nation to interact within the type of financial and strategic outreach that China has undertaken by initiatives just like the BRI. Nonetheless, it seems that India, the US, and quite a lot of different technologically and financially succesful nations can collectively dent China’s efforts by providing the growing world a viable various. The IMEC companion nations seem to have the precise substances to trigger some concern in Beijing.