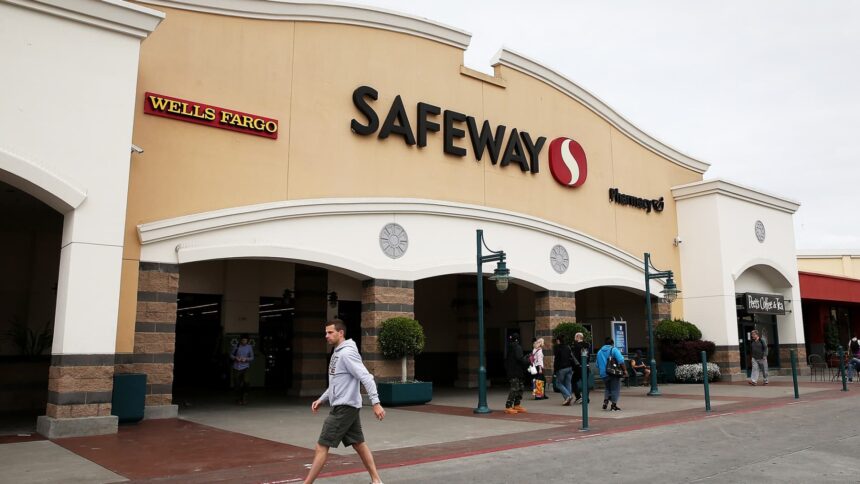
Prospects at a Safeway retailer in San Francisco.
Getty Photos
American banks have been shuttering branches positioned inside grocery store chains at a price seven occasions quicker than different areas amid the trade’s revenue squeeze and clients’ migration to digital channels.
Banks closed 10.7% of their in-store branches within the yr ending June 30, in line with Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation information. The closure price for different branches was 1.4% throughout that interval.
Most branches inside grocery shops are operated by regional banks, which have been below stress for the reason that March collapse of Silicon Valley Financial institution. PNC, Residents Monetary and U.S. Financial institution shut essentially the most in-store areas through the 12-month interval at chains together with Safeway and Cease & Store. Amongst retailers, Walmart homes essentially the most financial institution branches with 1,179, in line with an S&P International report launched this week.
Whereas the monetary trade has been closing branches for years, the tempo accelerated sharply in 2021 after the Covid-19 pandemic turbocharged the adoption of cell and on-line banking. That yr, banks closed almost 18% of their in-store branches and three.1% of different areas, S&P International mentioned.
“In-store branches have fallen out of favor at many banks,” mentioned Nathan Stovall, head of monetary establishments analysis at S&P International Market Intelligence. “We have seen banks look to shrink their department networks, with a give attention to slicing less-profitable branches that generate much less buyer visitors and fewer loans and excessive internet price accounts.”
Banks started constructing branches inside supermarkets in the 1990s as a result of the scaled-down areas have been far cheaper to arrange than common areas. However the trade now views branches as a spot to entice clients with wealth administration accounts, bank cards and loans relatively than only a place to withdraw cash, and that favors full-size branches.
The tempo of closures has slowed for the reason that 2021 peak however continues to be at an elevated degree in comparison with earlier than the pandemic. For example, in 2019, banks shut 4.2% of in-store areas and 1.7% of different areas.
The strikes come because the trade is adjusting to increased funding prices as clients have moved balances into higher-yielding choices equivalent to cash market funds. U.S. banks registered a 15% decline in deposits from in-store branches, whereas deposits at different branches fell 4.7% within the yr ending June 30, in line with the FDIC.
Do not miss these CNBC PRO tales: