An enormous seismic occasion on Mars—a “marsquake”—that shook the Pink Planet final yr had an surprising supply, stunning astrophysicists from world wide. They suspected a meteorite strike. As an alternative, monumental tectonic forces inside Mars’s crust, which brought on vibrations that lasted for six hours, brought on the quake and never a meteorite strike. The findings are described in a study published October 17 in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
[Related: Two NASA missions combined forces to analyze a new kind of marsquake.]
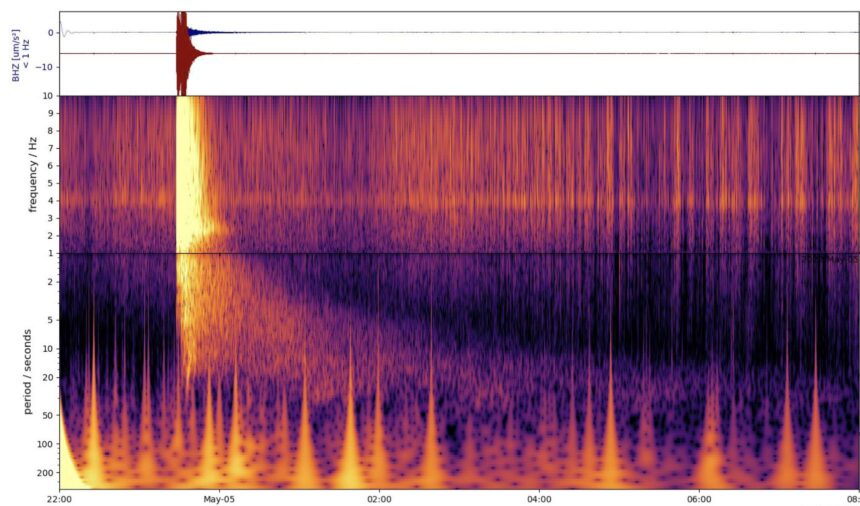
NASA’s InSight lander recorded the magnitude 4.7 marsquake on May 4, 2022, which scientists named S1222a. Its seismic sign was just like these of earlier quakes that had been brought on by meteorite impacts, so the workforce started to seek for an affect crater.
Within the new study, a workforce from the College of Oxford labored with the European House Company, Chinese language Nationwide House Company, the Indian House Analysis Organisation, and the United Arab Emirates House Company to scour greater than 55 million sq. miles on Mars. Every group examined the info coming from its personal satellites to search for a crater, mud cloud, or different signature of a meteorite affect. As a result of the search got here up empty, they now imagine that S1222a was brought on by the discharge of giant tectonic forces from inside the Martian inside.
That doesn’t imply Mars’s tectonic plates are shifting the best way they do throughout an earthquake. The perfect obtainable proof suggests the planet is remaining nonetheless. “We nonetheless assume that Mars doesn’t have any lively plate tectonics immediately, so this occasion was seemingly brought on by the discharge of stress inside Mars’ crust,” examine co-author and College of Oxford planetary geophysicist Benjamin Fernando said in a statement. “These stresses are the results of billions of years of evolution; together with the cooling and shrinking of various elements of the planet at completely different charges.”
Whereas Fernando explains that scientists don’t absolutely perceive why some elements of Mars appear to have extra stress than others, these outcomes will help them examine additional. “Sooner or later, this data could assist us to know the place it could be secure for people to dwell on Mars and the place you may wish to keep away from!” he stated.
S1222a was one of many final occasions recorded by NASA’s InSight mission earlier than its finish. The InSight lander launched in Might 2018 and survived “seven minutes of terror” to the touch down on Mars, the place it studied the planet’s inside and seismology for years. The final of the spacecraft’s knowledge was returned in December 2022, after rising mud accumulation on its photo voltaic panels brought on InSight to lose energy.
[Related: InSight says goodbye with what may be its last wistful image of Mars.]
In its four years and 19 days of service, InSight recorded greater than 1,300 marsquakes. Not less than eight of these events were from a meteorite impact; the biggest two fashioned craters that had been virtually 500 toes in diameter. If the S1222a occasion was fashioned by an affect, the workforce estimates that the crater to be would have been at the least 984 toes in diameter.
The workforce is making use of data from this examine to different work, together with future missions to our moon and the tectonics that are similar to California’s famed San Andreas fault positioned on considered one of Saturn’s moons named Titan. In addition they hope that it encourages further main worldwide collaborations to check the Pink Planet and past.
“This has been an amazing alternative for me to collaborate with the InSight workforce, in addition to with people from different main missions devoted to the examine of Mars,” examine co-author and New York College Abu Dhabi astrophysicist Dimitra Atri said in a statement. “This actually is the golden age of Mars exploration!”