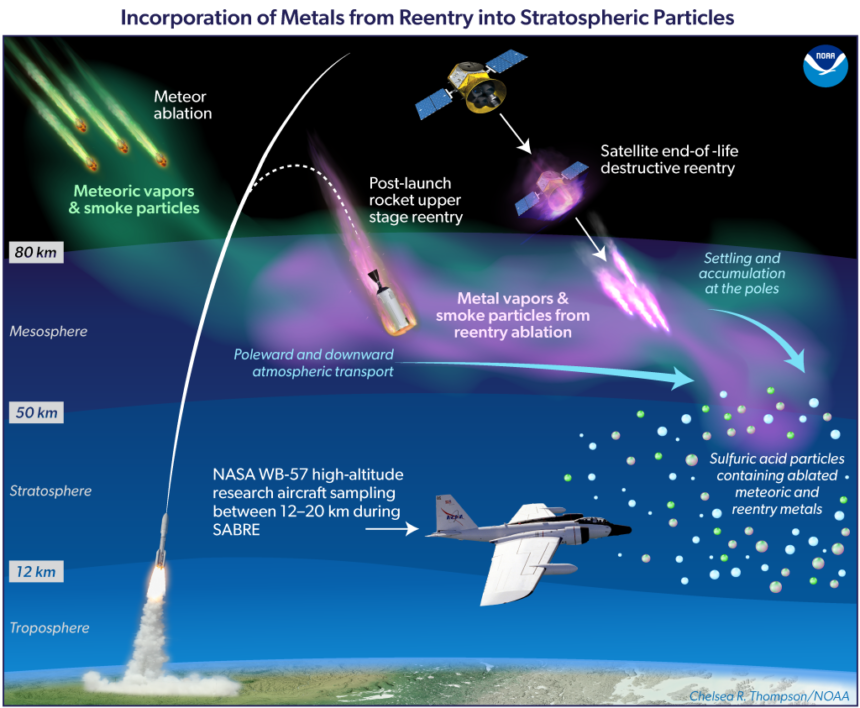
People have been altering the ambiance from Earth’s floor for almost two centuries—however now within the House Age, we’re altering it from outer house, too. Atmospheric scientists not too long ago discovered traces of sudden metals within the stratosphere, the second-lowest layer of the ambiance the place ozone resides and meteors deplete into taking pictures stars. The researchers decided that this air pollution got here from spacecraft as they reenter Earth’s ambiance, in analysis revealed final week within the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
This research is “the primary observational proof that house actions are a really important supply of particulate air pollution to the stratosphere” says Slimane Bekki, an atmospheric scientist at LATMOS not concerned within the new work. “Extra importantly, no person is aware of the impacts of those particles on the ozone layer,” he provides, stating the significance of this molecule in shielding people from harmful UV radiation.
Often, mission planners’ most important concern is to make sure that house particles doesn’t hit the bottom, the place it might harm folks or buildings—however, as this analysis factors out, what evaporates within the stratosphere might nonetheless be making an impression, even when it’s not a literal one. That materials has to exist someplace, and it seems prefer it’s lingering within the stratosphere. “We’re discovering this human-made materials in what we think about a pristine space of the ambiance. And if one thing is altering within the stratosphere—this steady area of the ambiance—that deserves a more in-depth look,” stated co-author and Purdue atmospheric scientist Dan Cziczo in a press release.
[Related on PopSci+: Rocket fuel might be polluting the Earth’s upper atmosphere]
The analysis group flew via the stratosphere throughout the continental US in plane specifically designed to fly at excessive altitudes, geared up with air-analyzing devices of their nostril cones. These distinctive planes— NASA’s ER-2 and WB-57—cruise at round 65,000 toes, nearly double the altitude of typical passenger jets. Flying as excessive as 70,000 toes, the analysis craft can go above 99 % of the mass of Earth’s ambiance.
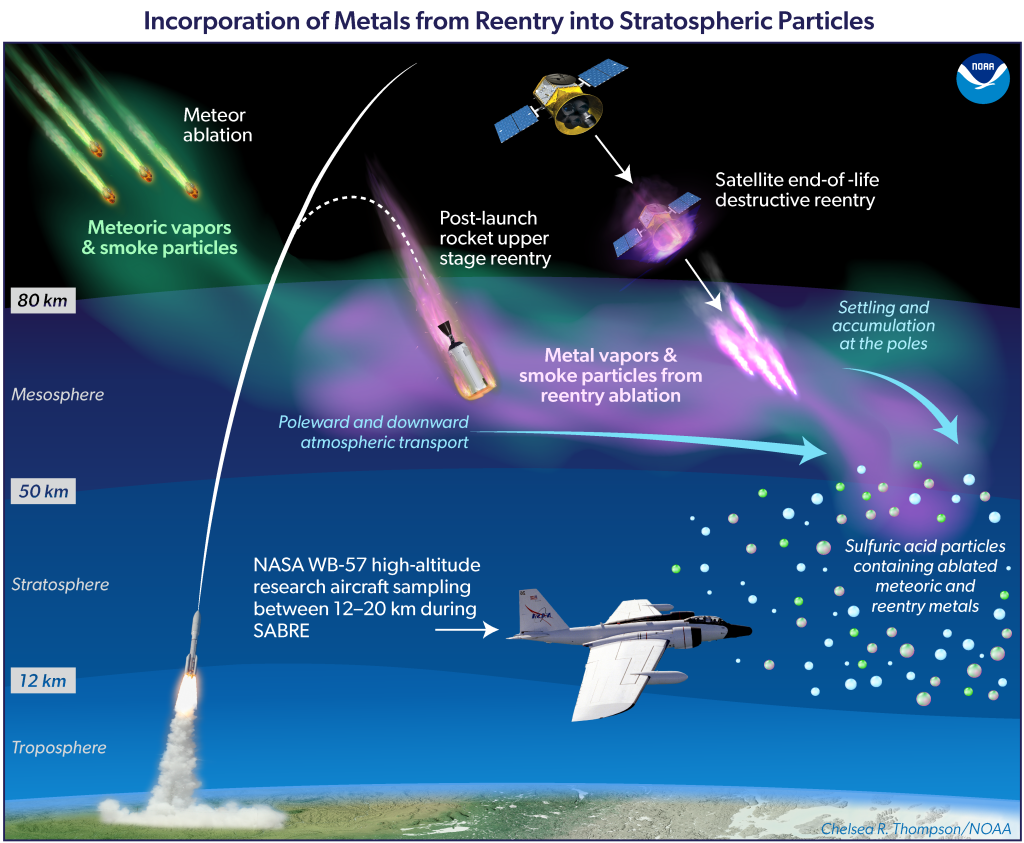
Inside the stratosphere, the amassing tools on these planes recorded traces of the heavy metals niobium and hafnium. These components aren’t discovered naturally within the ambiance, however they’re sometimes utilized in rockets and spacecraft shells. The group additionally measured higher-than-expected concentrations of over 20 metals, together with copper, lithium, aluminum, and lead. All advised, about 10 % of aerosol particles within the stratosphere include metals.
Atmospheric scientists aren’t positive precisely how these modifications will have an effect on Earth. The stratosphere accommodates tiny blobs of sulfuric acid, which are actually infused with the metals from outdated spacecraft. The presence of these metals might change the chemistry of the stratosphere, together with how large the sulfuric acid drops develop. Even small tweaks excessive up might have an effect on the way in which mild bends, the switch of warmth, or how crystals of ice develop.
The large query is how these modifications will have an effect on human life on the floor. Sadly, there’s no clear reply to that, however up to now small stratospheric modifications have led to large impacts—like including CFCs that ate away on the ozone layer. Finally, there could should be extra environmental precautions for spaceflight to stop hurt to the stratosphere.
[Related: This beautiful map of Earth’s atmosphere shows a world on fire]
“The one method for these particles to not seem within the higher ambiance is for the satellites to not be launched within the first place,” explains College of Exeter atmospheric scientist Jamie Shutler, who was not a part of the analysis group. “The doable methods ahead are to launch much less, make the satellites final for longer (so we have to launch much less), or encourage business to make the constituents of satellites public data (so we will information producers as to the potential dangerous results).” He provides that this new discovering “confirms our concern” about stratospheric contamination.
However earlier than we will clear up this drawback, “the idea that reentry can have an effect on the stratosphere must be considered,” says lead creator Daniel Murphy, atmospheric scientist at NOAA. He emphasised that this concept continues to be extremely new and would require way more analysis to grasp the dimensions and potential penalties of this air pollution.
Potential impacts are anticipated solely to develop as the speed of spacecraft launches and reentries speed up. Within the final 5 years, house businesses and personal corporations have launched greater than 5,000 satellites, famous Martin Ross, co-author on the work and local weather scientist at The Aerospace Company, in a press launch. “Most of them will come again within the subsequent 5, and we have to know the way that may additional have an effect on stratospheric aerosols,” he stated. The group expects that the proportion of particles containing steel might develop from 10 to greater than 50 % within the subsequent few many years, particularly thanks to approaching plans to cut back house particles by hurling it again into the ambiance.
These efforts and upcoming launches, although, want to pay attention to the doable results on Earth—and researchers have to do extra work to find out the extent of these results. “Understanding our planet is likely one of the most pressing analysis priorities there’s,” stated Cziczo.