This text was initially featured on Known magazine.
Each human being begins out as only one fertilized egg. In maturity, that single cell has become about 37 trillion cells, a lot of which proceed to divide to create the identical quantity of contemporary human cells each few months.
However these cells face a formidable problem. The common division cell ought to copy – completely – 3.2 billion base pairs of DNA, about as soon as each 24 hours. The cell’s replication equipment does this splendidly, copying genetic materials at a hurried charge of about 50 base pairs per second.
Nonetheless, that is far too gradual to duplicate the entire thing human genome. If the cell’s copying machines began on the finish of every of its 46 chromosomes on the similar time, it might full the longest chromosome — number one, with 249 million base pairs — in about two months.
“The way in which cells naturally get round that is they begin replicating in a number of locations,” stated James Berger, a structural biologist at Johns Hopkins College College of Drugs in Baltimore, who co-authored an article on DNA replication in eukaryotes within the 2021 Annual Evaluation of Biochemistry. Yeast cells have a whole lot of attainable sources of replication, as they’re referred to as, and animals akin to mice and people have tens of 1000’s of them scattered all through their genomes.
“However that poses its personal problem,” says Berger, “which is, how are you aware the place to start out and the way do you time all the things?” With out precision management, some DNA might be copied twice, inflicting mobile pandemonium.
It is particularly necessary to maintain the DNA replication kickoff tight to keep away from that pandemonium. In the present day, researchers are shifting towards a full understanding of the molecular checks and balances which have developed to make sure that every origin initiates DNA copying as soon as, to provide precisely one fully new genome.
Do it proper, do it quick
Unhealthy issues can occur if replication would not begin accurately. To repeat DNA, the DNA double helix should open, and the ensuing single strands — every of which serves as a template for constructing a brand new, second strand — are susceptible to breakage. Or the method hangs. “You actually wish to resolve replication rapidly,” stated John Diffley, a biochemist on the Francis Crick Institute in London. Issues throughout DNA replication may cause the genome to turn out to be disorganized, which is usually a significant step on the street to most cancers.
Some genetic illnesses additionally consequence from problems with DNA replication. For instance, Meier-Gorlin syndrome, which includes brief stature, small ears, and small or no kneecaps, is brought on by mutations in a number of genes that assist set off the DNA replication course of.
It takes a tightly coordinated dance involving dozens of proteins earlier than the DNA copying machine begins replicating on the proper level within the cell’s life cycle. Researchers have a fairly good thought of which proteins do what as a result of they’ve managed to get DNA replication to happen in cell-free organic mixtures within the lab. They recreated the primary important steps in beginning replication using yeast proteins– the identical type used to make bread and beer – they usually mimicked a lot of the entire replication course of using human versions of replication proteinsat.
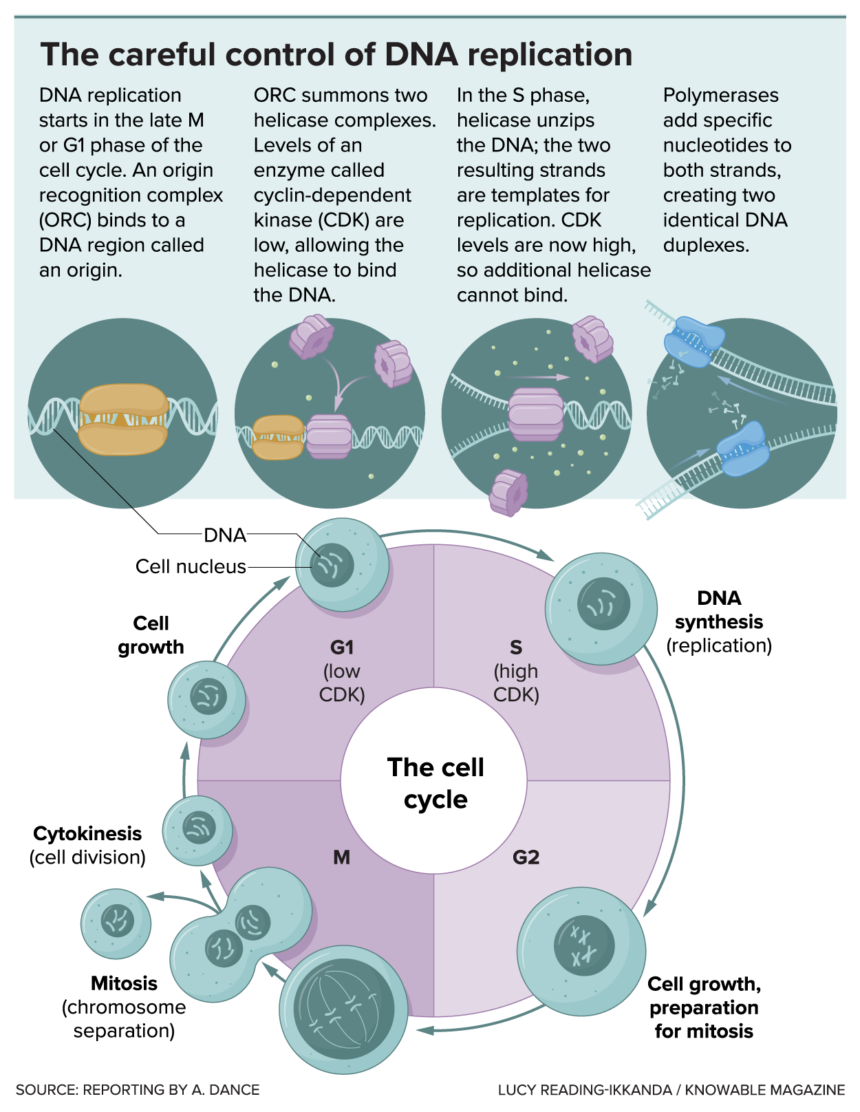
The cell controls the beginning of DNA replication in a two-step course of. The entire goal of the method is to regulate the actions of an important enzyme – referred to as a helicase – that unwinds the DNA double helix in preparation for copying it. In step one, inactive helicases are loaded onto the DNA on the origin, the place replication begins. Throughout the second step, the helicases are activated to unwind the DNA.
Executed (load the helicase)…
The method begins with a cluster of six proteins on the origin. This cluster is named ORC formed as a double-layered ring with a nifty notch that enables it to slip onto DNA strands, Berger’s crew has discovered.
In baker’s yeast, a favourite for scientists finding out DNA replication, these beginning websites are simple to acknowledge: they’ve a particular DNA core sequence of 11 to 17 letters, wealthy in chemical bases of adenine and thymine. Scientists have watched ORC seize maintain of the DNA after which slide on, scan for the origin string till he finds the proper place.
However in people and different complicated life kinds, the beginning websites aren’t so clearly delineated, and it isn’t totally clear what causes the ORC to quiet down and take maintain, says Alessandro Costa, a structural biologist on the Crick Institute who, with Diffley, wrote on the initiation of DNA replication within the 2022 Annual Evaluation of Biochemistry. Replication appears extra more likely to begin the place the genome—usually tightly coiled round proteins referred to as histones—has come free.
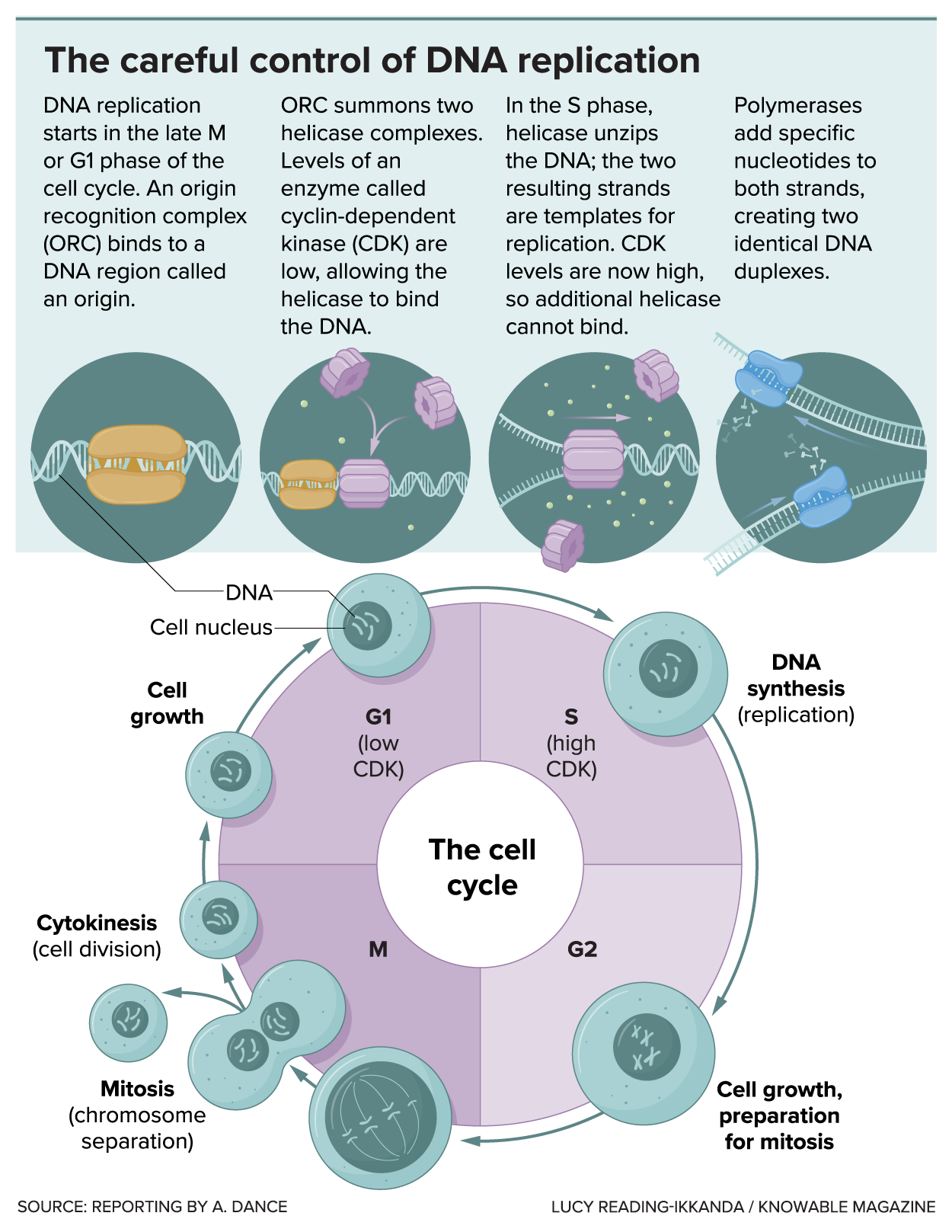
As soon as ORC has settled onto the DNA, it attracts a second protein complicated: one that features the helicase that may ultimately unwind the DNA. Costa and colleagues used electron microscopy to learn the way ORC lures in first a helicase, then another. The helicases are additionally ring-shaped and every opens to wrap across the double-stranded DNA. Then the 2 helicases shut once more, going through one another on the DNA strands, like two beads on a string.
At first they only sit there, like automobiles with no fuel within the tank. They haven’t but been activated and in the meanwhile the cell will proceed as regular.
Prepare (activate the helicase)…
Issues kick into excessive gear when an important molecule referred to as CDK waves the inexperienced flag, kick-starting chemical steps that lure in much more proteins. One is DNA polymerase – what Costa calls the “typewriter” that may construct new strands of DNA – which attaches to every helicase. Others activate the helicases, which may now burn vitality to haul the DNA alongside.
As this occurs, the helicases change form, pushing on one strand of DNA and pulling on the opposite. This places stress on the weak hydrogen bonds that usually maintain the 2 strands collectively by the bases – the As, Cs, Ts and Gs that make up the rungs of the DNA ladder. The 2 strands are torn aside. Costa and colleagues noticed how the 2 helicases unscrew the DNA between themthey usually’ve seen how the helicases maintain the unbound bases steady and out of the best way.
To go!
At first, each helicases are wrapped round each strands of DNA and may’t get very far this fashion as a result of they’re going through one another and simply run into one another. However then they every bear a place change, with one or the opposite DNA strand being spewed out of the ring. Now that they’re separate, they’ll crowd previous one another and replication is quick.
Every helicase motor alongside its single strand, in the wrong way from the opposite. They go away behind the origin and tear aside these hydrogen-bonded base pairs as they journey. The DNA polymerase is true behind it and copies the DNA letters as they’re free of their companions.
CDK’s second job is to stop any extra helicases from leaping onto the origin. Thus, there may be one begin of replication per origin, making certain appropriate copying of the genome, though copying doesn’t begin on the similar time in each place. All the strategy of DNA replication, in human cells, takes about eight hours.
There may be nonetheless lots to work out. For starters, the DNA being copied just isn’t a unadorned double helix. It’s wrapped round histones and connected to quite a few different proteins which might be within the strategy of turning genes on or off making RNA copies of the genes. How do these displacing proteins affect one another and stop them from getting in one another’s manner?
Along with this fascinating, elementary biology – a outstanding course of important to all life on Earth – there are implications for illnesses akin to most cancers. Scientists already know that misreplication can destabilize DNA, and an unstable genome susceptible to mutation could also be an early hallmark of most cancers improvement. And they’re further investigate hyperlinks between replication proteins and most cancers.
“I feel there are alternatives for therapeutic interventions for these methods,” says Berger, “as soon as we now have a very good understanding of how they work and what they appear to be.”
This text initially appeared in Known magazine, an impartial journalism initiative of Annual Evaluations. Join the newsletter.